1192. 查找集群内的「关键连接」
1192. 查找集群内的「关键连接
难度困难
力扣数据中心有 n 台服务器,分别按从 0 到 n-1 的方式进行了编号。
它们之间以「服务器到服务器」点对点的形式相互连接组成了一个内部集群,其中连接 connections 是无向的。
从形式上讲,connections[i] = [a, b] 表示服务器 a 和 b 之间形成连接。任何服务器都可以直接或者间接地通过网络到达任何其他服务器。
「关键连接」是在该集群中的重要连接,也就是说,假如我们将它移除,便会导致某些服务器无法访问其他服务器。
请你以任意顺序返回该集群内的所有 「关键连接」。
示例 1:
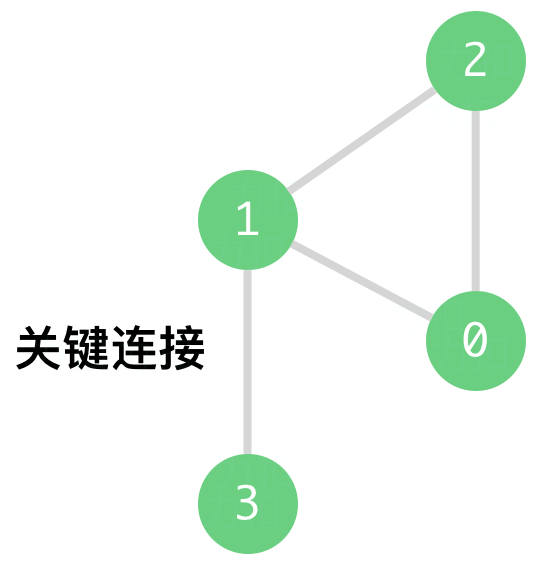
输入:n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[1,3]]
输出:[[1,3]]
解释:[[3,1]] 也是正确的。提示:
1 <= n <= 10^5n-1 <= connections.length <= 10^5connections[i][0] != connections[i][1]- 不存在重复的连接
函数签名:
func criticalConnections(n int, connections [][]int) [][]int分析
朴素解法(超时)
类似 1489-找到最小生成树里的关键边和伪关键边,最容易想到的解法是:枚举每一条边,检查不使用这条边,只用剩余的边能不能把所有点联通,可以借助并查集检查。
func criticalConnections(n int, connections [][]int) [][]int {
// 忽略边 conn 是否能联通所有节点
canConnectWithout := func(conn int) bool {
uf := NewUnionFind(n)
for i, v := range connections {
if i == conn {
continue
}
uf.Union(v[0], v[1])
}
return uf.set == 1
}
var res [][]int
for i, v := range connections {
if !canConnectWithout(i) {
res = append(res, v)
}
}
return res
}并查集相关代码如下
type UnionFind struct {
parent []int
set int // 连通分量数
}
func NewUnionFind(n int) *UnionFind {
ids := make([]int, n)
for i := range ids {
ids[i] = i
}
return &UnionFind{parent: ids, set: n}
}
func (uf *UnionFind) Union(x, y int) {
x, y = uf.Find(x), uf.Find(y)
if x == y {
return
}
uf.parent[x] = uf.parent[y]
uf.set--
}
func (uf *UnionFind) Find(x int) int {
for x != uf.parent[x] {
x, uf.parent[x] = uf.parent[x], uf.parent[uf.parent[x]]
}
return x
}并查集 Union 操作的复杂度可以看作均摊常熟级,整个过程时间复杂度是 O(E^2),E 指边的数量。复杂度非常高。
Tarjan 算法
Tarjan 算法是基于深度优先搜索的算法,用于求解图的连通性问题。原理不在这里细说。
func criticalConnections(n int, connections [][]int) [][]int {
// 构建图,方便迅速获知每个节点的相邻节点
graph := make([][]int, n)
for _, v := range connections {
graph[v[0]] = append(graph[v[0]], v[1])
graph[v[1]] = append(graph[v[1]], v[0])
}
// 为每个节点按照 dfs 访问时间编号, -1 代表还未被访问
id := make([]int, n)
for i := range id {
id[i] = -1
}
var dfs func(cur, parent, time int)
res := make([][]int, 0)
dfs = func(cur, parent, time int) {
if id[cur] != -1 {
return
}
id[cur] = time
for _, next := range graph[cur] {
if next == parent {
continue
}
dfs(next, cur, time+1)
// 如果 cur 和 next 不在环上, id[next] 最终就是 time+1
// 如果 cur 和 next 在一个环上, next 的访问时间会小于 cur 的访问时间
id[cur] = min(id[cur], id[next])
if time < id[next] {
res = append(res, []int{cur, next})
}
}
}
dfs(0, -1, 0)
return res
}时间复杂度:O(V+E),V为节点数,E为边数。
空间复杂度:O(V)。